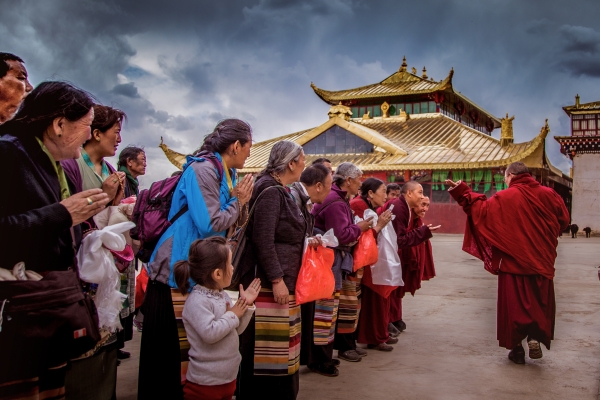
An Introduction to Buddhism: Five Basics
Did you know that nearly 80 percent of Buddhist people groups worldwide are considered least-reached? People in these groups don’t have access to a church that preaches the gospel in their language and worships in a way that’s relevant in their culture. Whether they live in the Far East or across the street, they won’t discover the eternal hope of Christ unless someone shares His good news with them.
Below are five must-know facts about Buddhism and its followers. (This is just a taste of the information and practical tips you’ll find in our updated Buddhism booklet!)
Buddhism is practiced by approximately half a billion people.
Over 490 million people worldwide are Buddhists. The majority live in Asia, but the influence of Buddhism is growing in the West. Over 660 people groups are primarily Buddhist and 30 of these groups live in North America.
Buddhism teaches there is no God.
Buddhism is non-theistic, meaning it doesn’t teach the existence of a God or gods. It’s the most prevalent religion that doesn’t include belief in a supreme being or beings. The Buddha did not claim to be a god, but merely the “enlightened one” who pointed the way.
In the Buddhist mindset, mankind’s great problem is suffering.
Buddhism teaches that suffering is the great problem of existence. The problem is not only that people suffer, but that this suffering extends over countless cycles of rebirth.
The Buddha summarized man’s predicament in the Four Noble Truths:
- Suffering is universal.
- Suffering is caused by desire.
- Suffering is cured by the elimination of desire.
- The Eightfold Path is the vehicle by which to eliminate desire.
Buddhists seek to escape suffering by reaching nirvana.
Nirvana, which means “extinguish” or “quench,” is a state of being reached by attaining enlightenment. In it, a person becomes unbound from the cycle of rebirth and is able to escape from suffering.
Different schools of Buddhism teach varying methods for ceasing to produce karma and achieving nirvana, including meditation, chanting, good works and following the Noble Eightfold Path. This path consists of eight right actions or states of mind that involve wisdom, ethical conduct and concentration.
Buddhism is diverse.
As Buddhism spread, it was influenced by a variety of indigenous beliefs, practices and worldviews. The way it’s practiced today reflects its inclusiveness and malleability. For example, different branches of Buddhism emphasize varying types of worship and accept different writings as authoritative.
Theravada, Mahayana and Vajrayana are usually considered the three major branches of Buddhism. However, there are numerous other subdivisions, each with its own traditions.
As followers of Christ, we have a treasure in God and His kingdom. At Christar, it is our joy to communicate the unsurpassed value of this treasure by serving the needs of others through our lives, professions, skills and words, as well as to equip followers of Jesus to reach out to the least-reached in their neighborhoods and around the world. Our booklet “Buddhism: An Introduction and Guide to Sharing Christ with Buddhists” provides practical tips for sharing Jesus with a Buddhist friend and offers an overview of Buddhist beliefs and practices. It will help you pray for Buddhists and Christar workers serving among them, as well as help you reach out to Buddhists in your neighborhood.







































_1724957011_600x400.png)

